What is FIDO?

FIDO is an open authentication standard technology developed to provide user authentication services that are simpler and more secure than password methods on personal smart devices.
FIDO was developed by the FIDO Alliance to reduce excessive dependence on passwords. FIDO supports not only biometric based authentication such as fingerprints, faces, and irises, but also various authentication means such as USSB security tokens and PIN.
FIDO provides safe and convenient authentication to users and the advantage of establishing a standard based authentication service without redundant investment to service companies. The user may use the authentication means installed in the device such as a PC, a smartphone, or a tablet PC. Companies adopting FIDO can selectively apply the desired authentication method without additional cost depending on the security level for each service that requires authentication.
FIDO operates in a structure that authenticates remotely with the FIDO authentication server using a common UAF or FIDO2. therefore, regardless of the user authentication means of the FIDO authentication device, the FIDO authentication service may easily accept various authentication means only by changing the setting.
FIDO was developed by the FIDO Alliance to reduce excessive dependence on passwords. FIDO supports not only biometric based authentication such as fingerprints, faces, and irises, but also various authentication means such as USSB security tokens and PIN.
FIDO provides safe and convenient authentication to users and the advantage of establishing a standard based authentication service without redundant investment to service companies. The user may use the authentication means installed in the device such as a PC, a smartphone, or a tablet PC. Companies adopting FIDO can selectively apply the desired authentication method without additional cost depending on the security level for each service that requires authentication.
FIDO operates in a structure that authenticates remotely with the FIDO authentication server using a common UAF or FIDO2. therefore, regardless of the user authentication means of the FIDO authentication device, the FIDO authentication service may easily accept various authentication means only by changing the setting.
FIDO is largely divided into three technical standard.
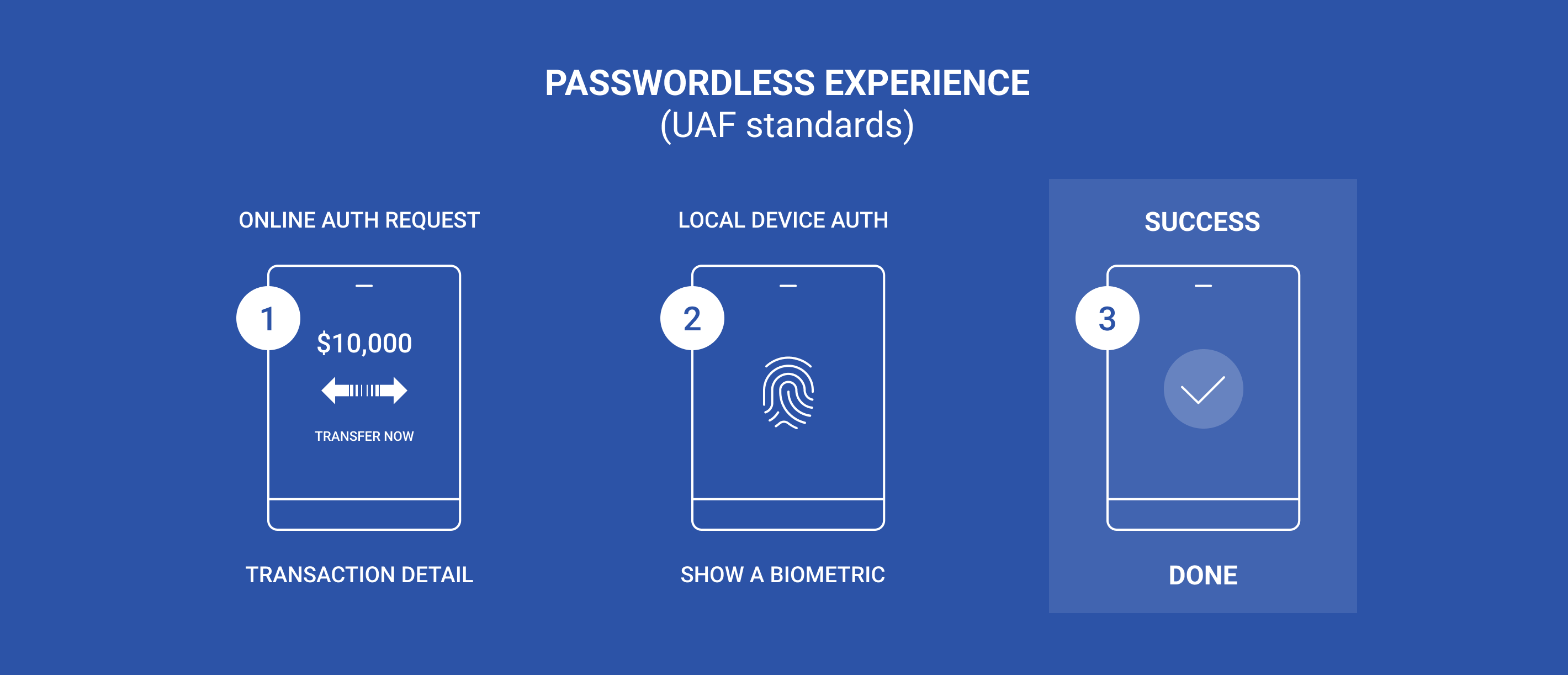
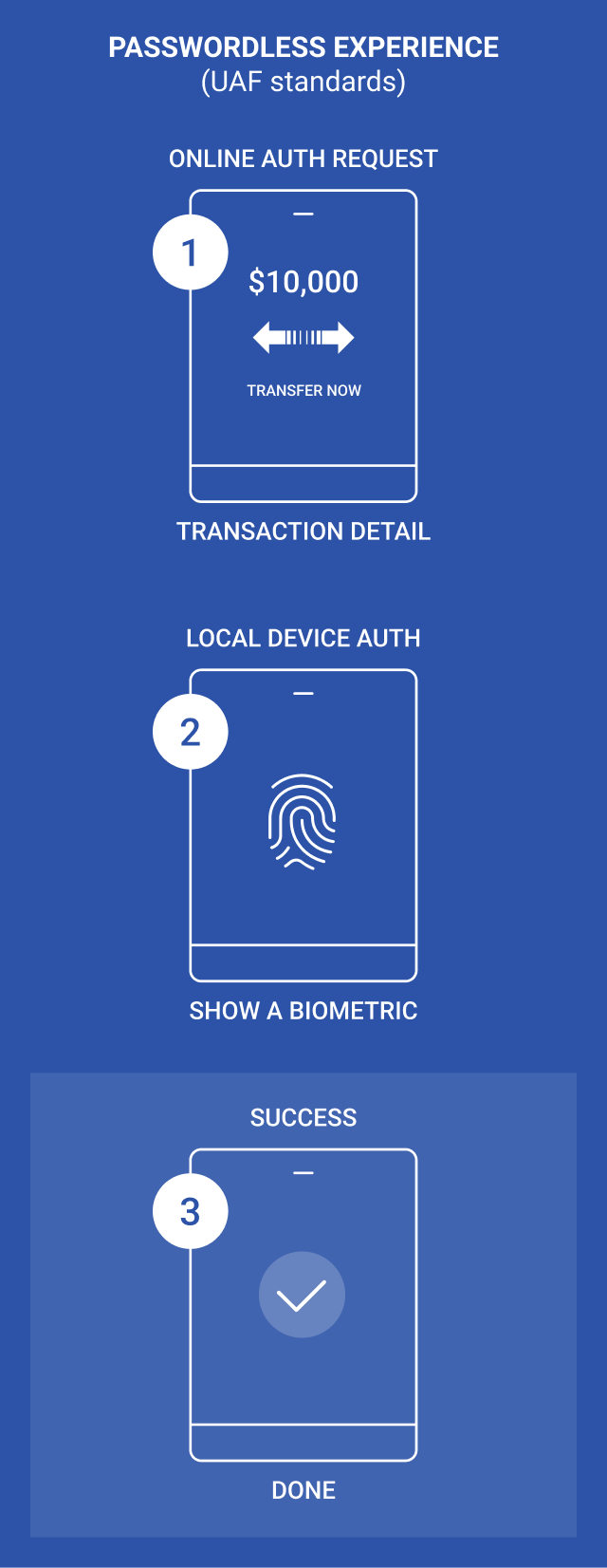
1. UAF (Universal Authentication Framework):
It is a technology that authenticates users in online services using apps using authentication means installed on their smart devices. Aimed to provide passwordless authentication using biometrics, PINs, and other local authenticators to authenticate users to online services without the need for passwords. Users must have a personal device, such as a computer or smartphone, and must register with an internet service to use UAF. This is device bound authentication and require re-register upon change of device such as phone.
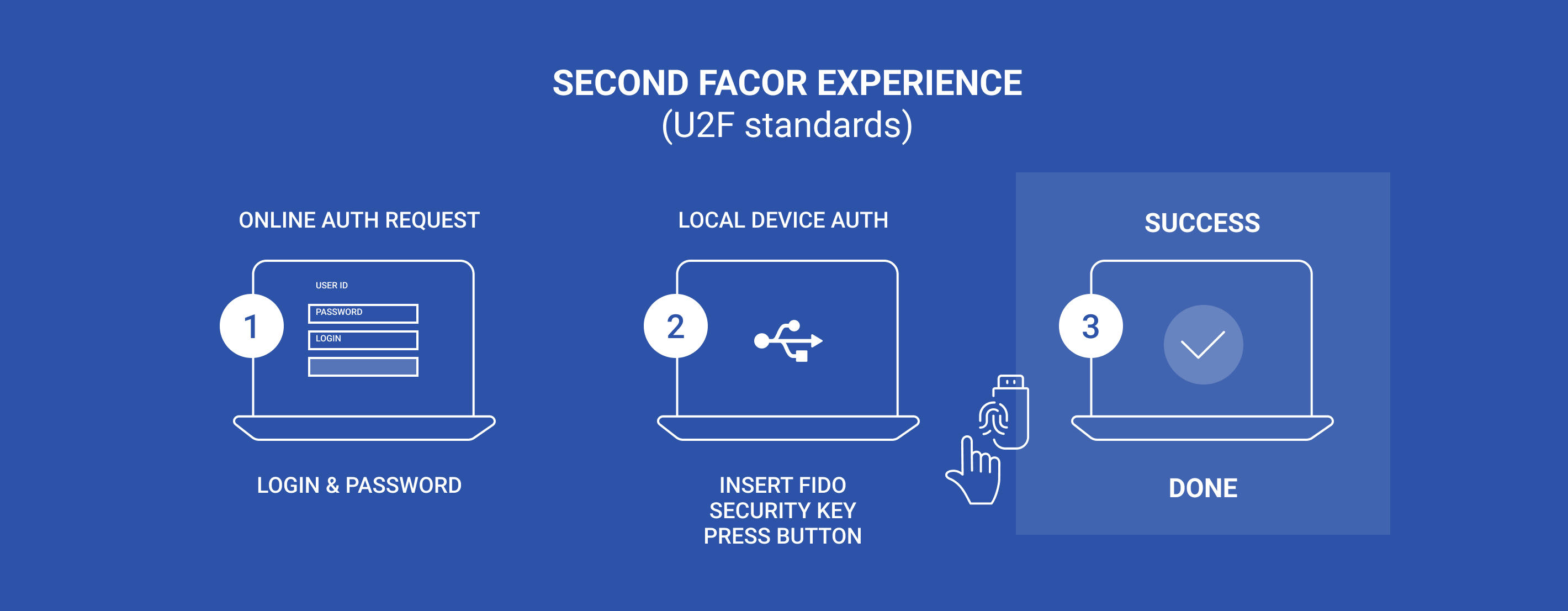
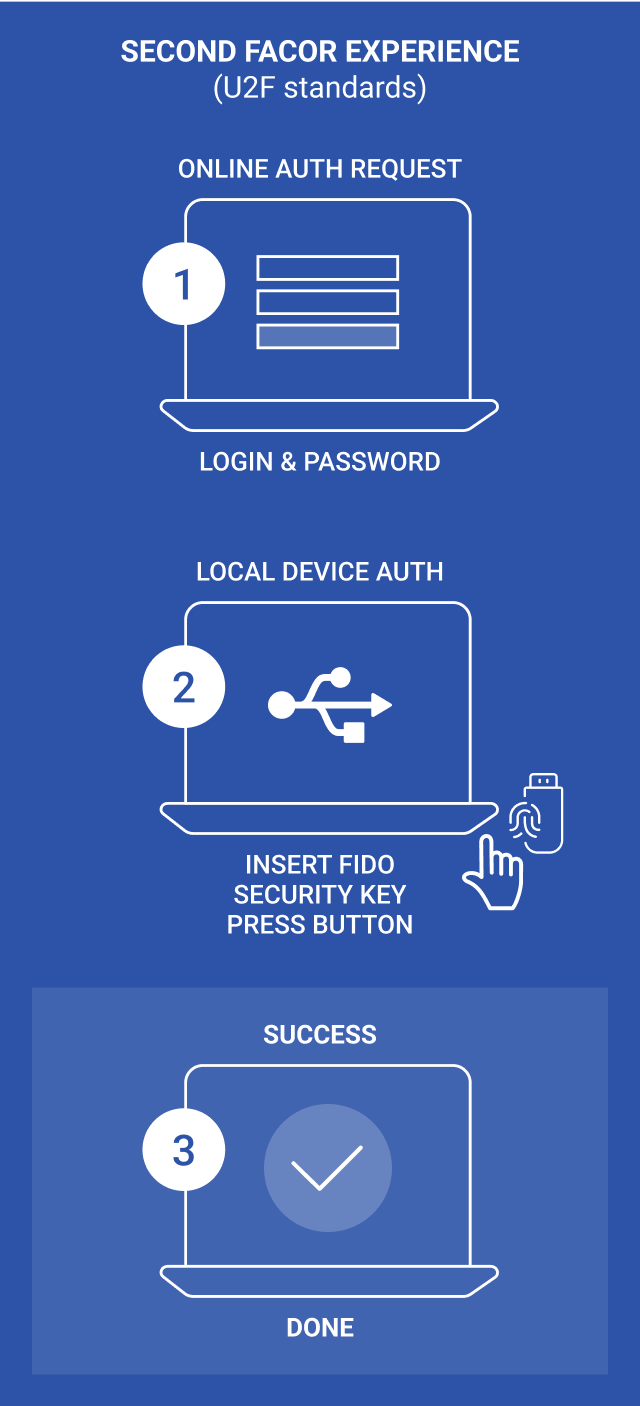
2. U2F (Universal 2nd Factor):
It is a technology that adds token-based authentication as secondary authentication when a user logs in on the website. It supports the U2F standard in Google Chrome browsers. Rather of replacing traditional password-based security, the FIDO U2F protocol complements it. Something they are familiar with, such as their account and password. They have something, such as a registered fob (a small security hardware device with built-in authentication used to control and secure access) or USB device through external hardware security keys, providing a stronger form of authentication.
3. FIDO2:
It supports the use of various authentication means such as token based authentication in web browsers. For example, it is possible to log in to a website through a fingerprint recognition device on a laptop. Since W3C completed the standard in 2019, most web browsers support FIDO2. FIDO2 includes the CTAP for communication between authentication devices and web browsers or OS platforms.
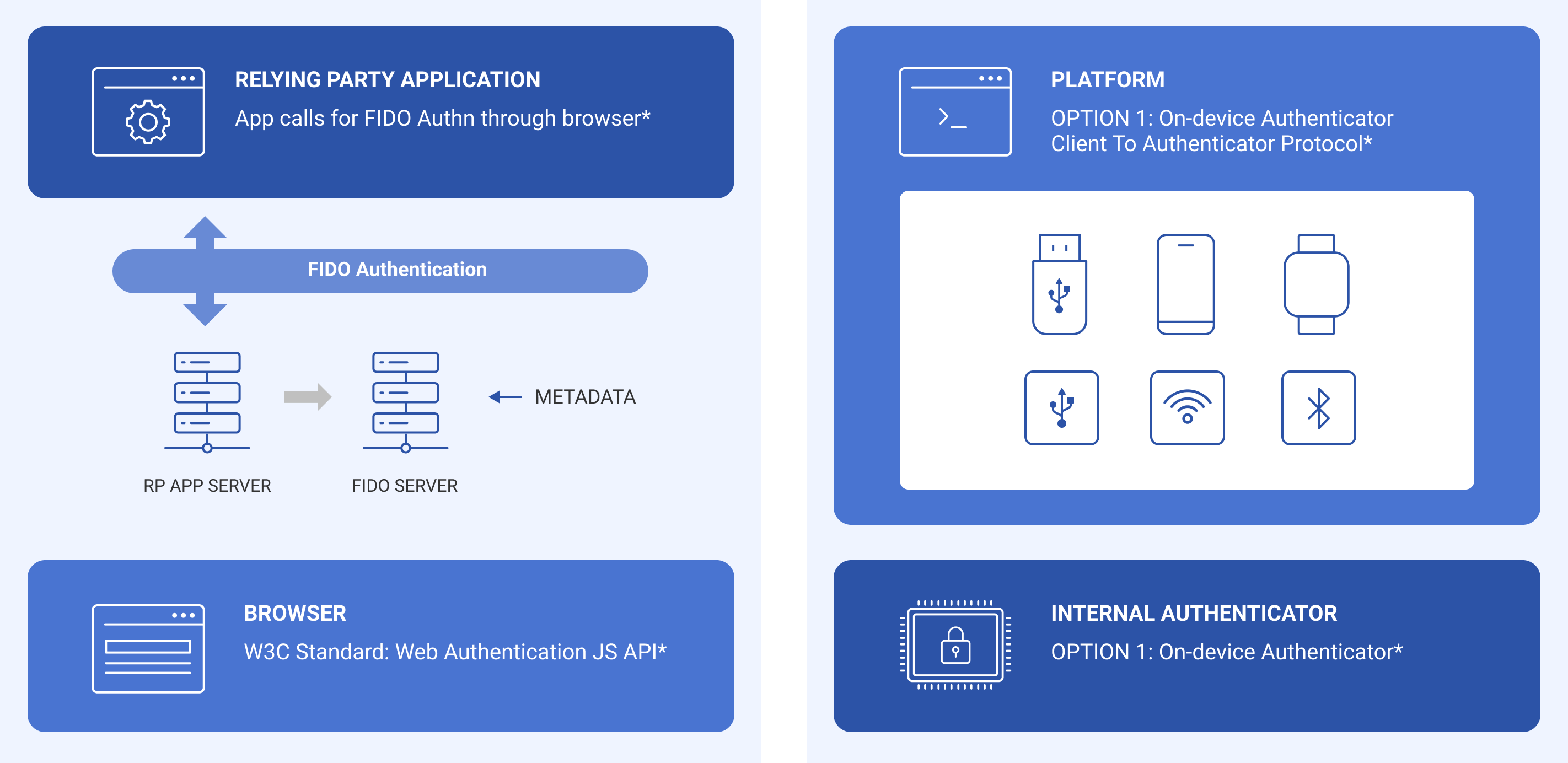
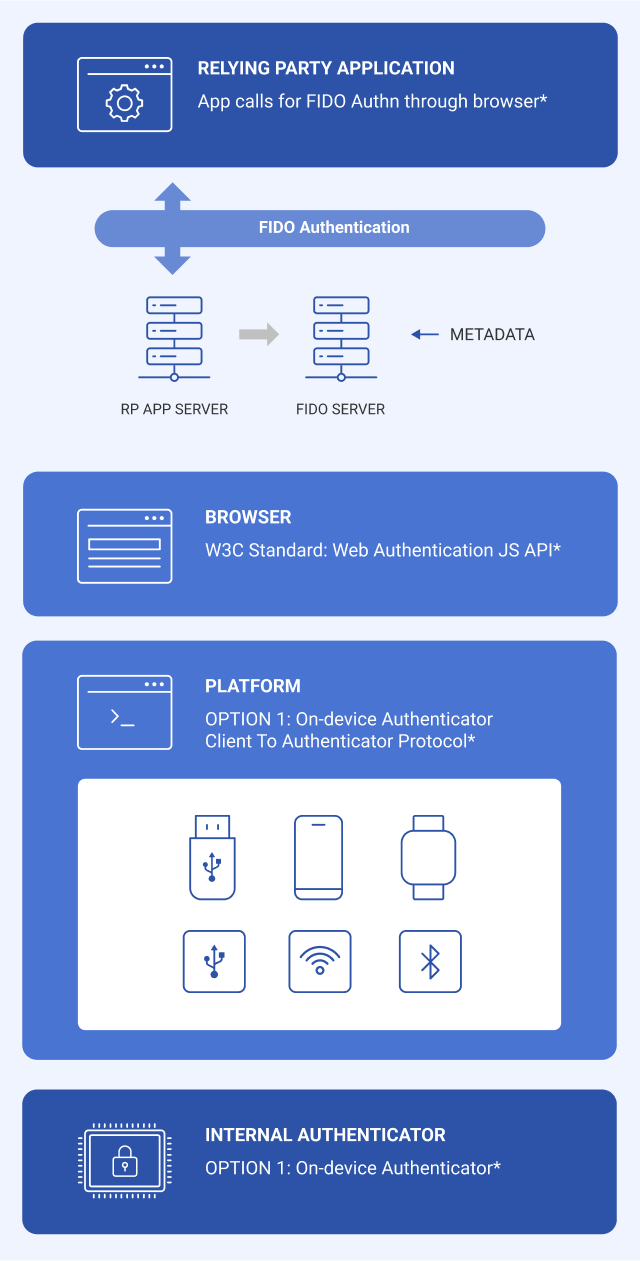
*FIDO2 Project





